- Washington’s
desire to “close out” the conflict ahead of domestic political cycles and
elections;
- A
strategy aimed at reducing U.S. involvement in foreign wars;
- A
shift toward prioritizing competition with China.
- Accepting
the plan = strategic defeat;
- Rejecting
the plan = risk of losing American support.
- internal
crisis and widespread public discontent,
- potential
political turbulence,
- de
facto acknowledgment of defeat.
- The
plan strengthens Russia’s position;
- It
sets a dangerous precedent: a major power changes borders by force;
- It
leaves Europe facing an aggressive Russia without a strong Ukraine as a buffer;
- It
undermines NATO as the core guarantor of collective security.
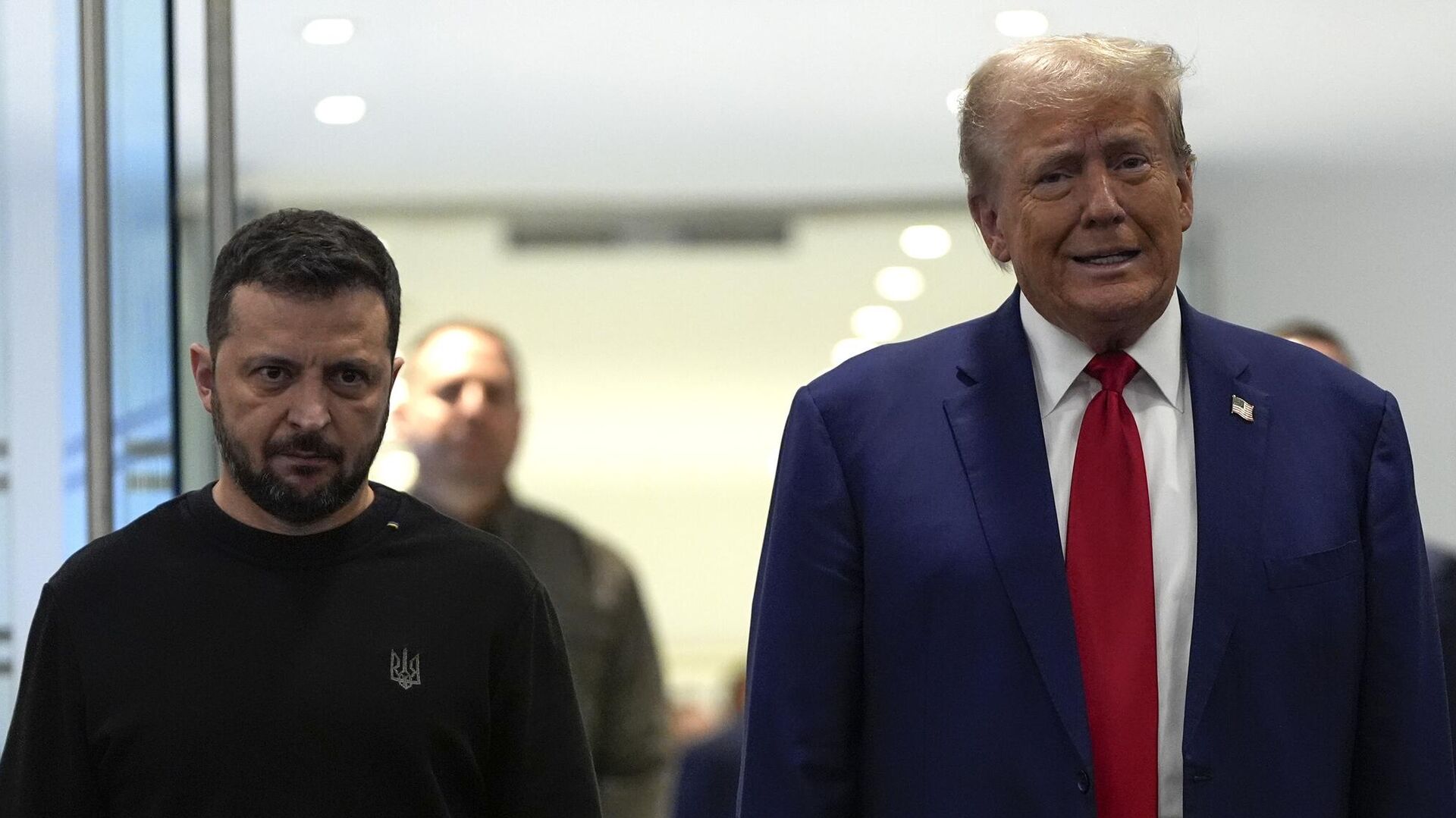
The U.S. Increases Pressure on Kyiv: What Lies Behind the American Peace Plan and Why It Alarms Europe?

Washington has sharply
intensified its efforts to promote its own peace plan for Ukraine. U.S.
President Donald Trump has demanded that Kyiv approve the proposed 28-point
document within a week, threatening to halt military assistance — a critical
resource for Ukraine’s defense effort.
A
statement by Volodymyr Zelensky on November 21 marked an acknowledgment that Ukraine
now faces a harsh and risky choice: either follow the American line,
sacrificing part of its sovereignty and strategic ambitions, or risk a rupture
with its main ally.
Meanwhile,
European capitals are voicing concern: the proposed framework for ending the
war is not merely a compromise — it radically shifts the regional balance of
power in Moscow’s favor.
The
plan consists of 28 provisions, including the following:
1. Ukraine’s renunciation of NATO membership. This
aligns with a long-standing Russian demand and effectively establishes a “zone
of limited sovereignty” for Ukraine in the security sphere.
2. A significant reduction of the Ukrainian
Armed Forces. Essentially, this amounts to demilitarization
under international supervision — a step that would leave Kyiv strategically
vulnerable.
3. Territorial concessions to Russia. The
plan envisions Ukraine relinquishing control over several territories that
Russia already occupies de facto.
4. International monitoring and security
guarantors. Yet the system of guarantees is vaguely
defined — there is no clear mechanism capable of protecting Ukraine from
renewed aggression.
5. Partial lifting of sanctions on Russia. According
to European officials, this condition threatens Western unity.
Overall,
the contents of the plan substantially reflect Moscow’s position and would
force Ukraine into a “freeze” of the conflict rather than a genuine resolution.
The
U.S. president has given Kyiv one week — until Thanksgiving — to accept the
document. The threat of suspending military aid turns the proposal into an
effective ultimatum. For Ukraine, this is critical, given that 70–80%
of its modern air defense systems are American-made, more than 50%
of ammunition comes from U.S. supplies, and U.S. intelligence
and surveillance capabilities are essential to battlefield operations. Thus,
the termination of American support amid escalating hostilities would
dramatically weaken Ukraine’s defense capacity.
Reasons behind U.S. pressure:
Zelensky
stated that Ukraine faces a “very difficult choice”. Diplomatically phrased,
the meaning is unambiguous:
Ukrainian
leadership understands that agreeing to these concessions would lead to:
Yet refusing the plan is also fraught with severe consequences for the country’s defense capabilities. European capitals — especially in Eastern Europe — have expressed serious concern.
Europe’s main objections:
European
leaders fear that a frozen conflict would lead to a renewed war within 2–3
years, allow Russia to regroup and restore resources, and diminish U.S.
influence in Europe, creating a strategic vacuum. Thus, the U.S. plan is viewed
in the EU as a threat to Europe’s broader security architecture.
Strategic risks for Ukraine:
1. Loss of territory and strategic initiative. The
plan cements a status quo favorable to Russia.
2. Loss of key security guarantees. Abandoning
NATO membership without credible alternatives leaves Ukraine strategically
exposed.
3. Internal political instability. A
society shaped by years of war is unlikely to accept such concessions.
4. Weakening of the international coalition. The
U.S. applies pressure — Europe resists — Western unity begins to fracture.
The American peace plan is a proposal to
end the war at any cost — and that cost falls on Ukraine. It reflects U.S.
priorities, but not the interests of Kyiv or the long-term strategy of Europe. Ukraine
now finds itself in a uniquely difficult position: heavily dependent on the
United States, yet unable to accept conditions that would erode its
sovereignty. The question now is whether Ukraine — and the entire Western
alliance — can maintain unity in the face of pressure, war, and geopolitical
fatigue.
 Latest news
Latest newsThe Use of the “Oreshnik” Missile and a New Phase of Escalation Around Ukraine
09.Jan.2026
Solidarity Deferred: Croatia and Romania’s Dangerous Retreat
08.Jan.2026
Azerbaijan’s Eurasian Initiative: Ambitions, Challenges, and Doubts
07.Jan.2026
The Great Rotation: Personnel Reshuffles in Ukraine’s Leadership
06.Jan.2026
The United States Did Not Confirm an Alleged Ukrainian Attack on Putin’s Residence
05.Jan.2026
The Trans-Caspian Fiber Optic Cable: A Digital Milestone Connecting Europe and Asia
04.Jan.2026
Georgia Hopes for a Review of Venezuela’s Recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia Amid Ongoing Crisis
04.Jan.2026
Ukraine’s Allies Discuss Security and the Future of a Peace Settlement
03.Jan.2026
Iran Amid a Growing Domestic Crisis: Causes, Dynamics, and External Factors
03.Jan.2026
The South Caucasus in the Context of Expanding External Involvement
02.Jan.2026

 14 Jan 2026
14 Jan 2026








